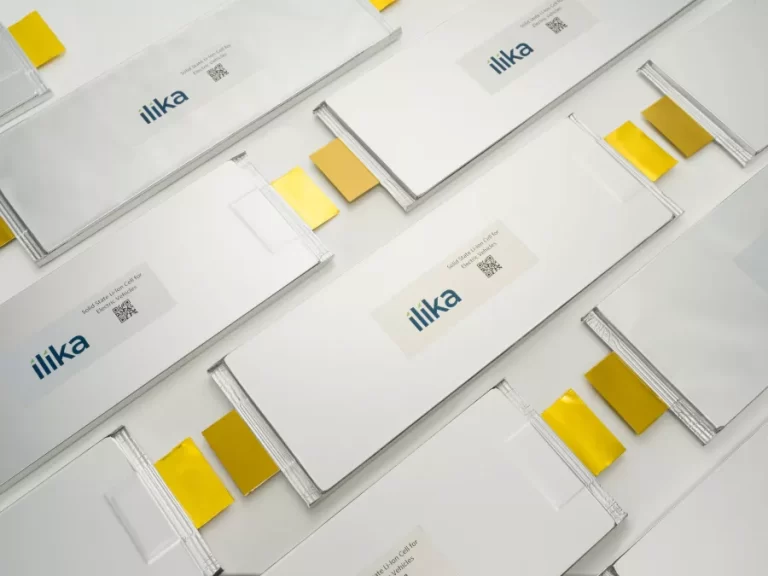
Ilika plc (LON:IKA), a pioneer in solid-state battery technology and materials innovation, announced today its full-year results for the year ended 30 April 2018.
Operational highlights:
· Implementation of Stereax® development programmes with three commercial partners:
o Deployment in miniature medical implants with a leading bioelectronics company
o Collaboration with Lightricity (ex-Sharp) to integrate Stereax® solid state batteries with photovoltaic technology
o Deployment of Stereax® M250 cells with Titan Wind Energy, in condition monitoring devices for wind turbines
· Collaboration with global eight OEM’s to develop new functional materials:
o Protected anodes for lithium sulphur batteries with Johnson Matthey
o Advanced battery materials and fuel cell catalysts that can power future zero-emissions and carbon-neutral vehicles with Toyota Research Institute
o Photonic materials for high capacity Hard Disk Drives with Seagate
o P-type semiconductors for flexible integrated circuits with PragmatIC and Arm
o Superalloys with Rolls Royce
o Self-healing alloys with BAE Systems and GKN
· Award of ISO9001 certification to Ilika’s quality management system.
· Post year end: offer of £4.1m grant funding from the Faraday Challenge to develop large format solid-state cells for automotive in collaboration with Honda, Ricardo, McLaren and A123 Batteries.
Financial highlights:
· Revenues £2.1m (2017: £1.1m)
· Loss for the year £2.9m (2017: £3.5m)
· Loss per share 3.7p (2017: 4.8p)
· Cash, cash equivalents and bank deposits of £2.8m (2017: £5.4m)
Commenting on the results Ilika Plc Chairman, Mike Inglis, said: “The past year has seen strong progress from Ilika both operationally and financially. The Stereax® pilot line has produced samples of Ilika’s batteries for evaluation by 12 partners around the world. Feedback from those evaluations has been positive and underpins our ongoing commercialisation efforts. Following market demand we have extended our roadmap to include large format Stereax® cells for automotive power and I was delighted to see that Innovate UK has offered to support Ilika in two of the Faraday Challenge automotive collaborations with £4.1m of funding working with key industry players such as Honda, McLaren and Ricardo. Financially, revenue climbed over the £2m mark, with expectations of further growth in the year to come.”
STRATEGIC REPORT
The Directors present their Strategic Report for the year ended 30th April 2018.
Principal Activities
Ilika plc is the holding company for Ilika Technologies Limited, a pioneer in solid-state battery technology and materials innovation. Ilika has developed ground-breaking solid-state battery technology (Stereax®). The Stereax® roadmap commences with miniature batteries designed to meet the demands of powering wireless devices, referred to as “the Internet of Things (IoT)”. Stereax® technology was developed on Ilika’s unique, patent protected high throughput materials development platform, which accelerates the discovery of new and patentable materials for identified end uses in the automotive, aeronautical and electronics sectors.
Business Strategy
The Company’s mission is to have its Stereax® solid-state batteries integrated into market-leading products sold by leading commercialisation partners around the world. The Company generally expects these end-products to fit into or create end-markets worth in excess of $1 billion per year, in which the Directors believe a number of the Company’s commercialisation partners are positioned to have a leading share.
The Company’s revenue model involves three phases of activity: a) commercially-funded and grant-funded development projects; b) IP licensing; and c) receipt of royalties when products incorporating Ilika IP reach market. Ilika is currently in the first phase of activity, with its revenue being generated from a portfolio of development programmes. The Company has built a pipeline of licensing opportunities to support the start of its second phase of revenue generation.
The Company has developed its Stereax® batteries using its high throughput materials innovation platform. This platform uses automated processes to simultaneously deposit large arrays of systematically varying materials, which can be rapidly evaluated to determine their functional properties. In addition to the Stereax® product development and commercialisation work, the Company executes a small portfolio of programmes with large multinational companies to develop materials for the automotive, aerospace and electronic sectors.
Operating Review
Solid-State Batteries
Ilika has been working with solid-state battery technology since 2008 and has developed a type of lithium-ion battery, which, instead of using liquid or polymer electrolyte, uses a ceramic ion conductor.
Ilika’s solid-state batteries have a number of benefits over lithium-ion batteries, including the following:
· Non-flammable
· 6x faster to charge
· 2x energy density on a weight basis
· 10x lower leakage currents
Stereax® Technology Roadmap
Ilika elected to focus its initial cell development on miniature devices suitable for powering sensors, sometimes called IoT end-nodes. There are already up to 15 billion sensors on the planet and most of them are currently either hard-wired or powered by disposable coin cells. Hard-wired sensors are expensive to install because of the cost of cabling, but thereafter they have low maintenance costs. Sensors powered by disposable batteries are relatively cheap to install, but expensive to maintain because of the cost of the maintenance crews deployed to replace the batteries at regular intervals. Ilika’s miniature devices are designed to be combined with a small energy harvester (usually photovoltaic) to allow them to be recharged and therefore to operate for an extended period of time, usually up to ten years. This concept is designed to offer a low cost of installation compared to hard-wired devices combined with lower maintenance costs relative to using disposable coin cells.
IoT devices offer a different set of battery challenges compared to other electronic devices. They have similar pressures, such as cost and availability, but they also have some specific requirements:
o Small size in both footprint and thickness
o Ability to be trickle charged
o Charged only when an energy harvester can get energy
o Longer life span to match those of sensors and MCUs
o Support wider temperature ranges
Battery Product Launches
In 2016 and 2017, Ilika launched its Stereax® M250 and P180 solid state battery IP respectively. Both devices are designed to power IoT devices, with the P180 being specified to survive exposure to higher operating temperatures.
Relative to other miniature batteries, Ilika Stereax® batteries use patented materials and processes enabling superior energy density per battery footprint, up to 40% improvement on other solid-state solutions. Ilika’s batteries do not contain any free lithium which makes them more moisture resistant. The Stereax® M250 operates in a temperature range to over 100°C, 30°C higher than other solid-state products. The Stereax® P180 has the additional benefit of supporting a temperature up to +150°C. This higher temperature is required for many Industrial IoT and Automotive end applications enabling always on, self-charging energy efficient IoT solutions for more demanding environments. As the trend towards digitising industrial processes gathers momentum there is a growing requirement for components with enhanced tolerance to temperature, moisture and vibration.
Battery products under development
The Ilika Stereax® roadmap focuses on three main areas:
· Miniaturisation. This looks at progressively smaller footprints, down to mm-scale, delivering smaller currents (µAh), making them ideal for small sensor driven devices. The principal commercial pull for these batteries is coming from the medical device industry, accounting for about 50% of the value of Ilika’s licensing pipeline.
· Capacity. For the launch of both the M250 and the P180, Ilika designed and made some wireless sensor nodes measuring temperature, humidity and light intensity. The power requirements of sensors does vary, depending on the nature of the sensor. For example, a motion detector has a higher power requirement than a temperature sensor. In order to be able to power a wider range of devices, Ilika is increasing the energy footprint of its batteries. Increasing the amount of energy for a given active footprint can be achieved by utilising Ilika’s patented stacking feature, which allows multiple cells to be stacked on top of one another. The sector most interested in larger capacity devices is the Industrial IoT and this sector accounts for about 25% of the value of the licensing pipeline.
· Large format. Solid-state batteries are of great interest to the automotive industry. Indeed, Ilika first started working on solid-state materials through its collaboration with Toyota, which commenced in 2008. Many automotive companies now have solid-state cells on their electric vehicle roadmap and Ilika has experienced a rising number of inbound enquiries on the possibility of scaling its technology to address the opportunity to use solid state as a motive power battery. This topic is discussed further below.
Stereax Development and Deployment Projects
Ilika has secured three development and deployment programmes with global OEM’s:
Integrated energy harvester and battery
In December 2016, the company announced a two-year collaborative project with Sharp Laboratories of Europe (now known as Lightricity) to create an autonomous energy harvesting power source which will involve the integration of Ilika’s solid state battery with Lightricity’s photovoltaic (PV) technology creating the world’s first fully integrated thin-film power source. This integration project is aligned with the development track for increasing the capacity of Stereax batteries.
Miniature Medical Implant
In March 2017, the company announced a two-year collaborative project with a well-financed bioelectronics company to develop a battery for miniature medical implants to provide treatments for serious health conditions, through the body’s own nervous system. The programme is supported by Innovate UK and the Medical Research Council.
Wind turbine condition monitoring
In November 2017, Ilika announced a partnership to deploy Stereax powered devices for the condition monitoring of wind turbines with Titan Wind Energy, the largest manufacturer of wind turbines in China and the 4th largest globally.
Innovate UK Faraday Challenge
Innovate UK is expecting 50% of vehicle production by 2030 to be electric vehicles (EV) or plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEV). In July 2017, the UK government announced a £246 million commitment over 4 years for automotive battery development, covering cell manufacture, modules, battery pack design and deployment in vehicles. In November 2017, this was followed with the announcement of an £80m National Battery Manufacturing Development Facility in Warwick. Innovate UK is administering a series of competitions, designed to promote battery innovation. In a post year end development in June 2018, Ilika announced that it has been offered £4.1m of grant funding to participate in collaborations with Honda, Ricardo, McLaren and A123 Batteries.
The development of large format cells will require Ilika to build a lower cost printing platform, suitable for printing bulk materials. This will involve establishing a pre-pilot line at its facility in Southampton. It is anticipated that a second stage of scale-up to a pilot line could be achieved in collaboration with the National Battery Facility. Ilika currently expects to use its licensing model to commercialise the large format cells in the same way it is bringing its miniature batteries to market.
Patent Position
Building Ilika’s intellectual property portfolio in solid-state batteries has continued to be a focus this year. Three additional filings relating to solid-state batteries were made, covering electrolyte and electrode compositions as well as processing methods for singulating cells. In addition, three filings were made covering new superelastic and high-strength alloys from our self-healing alloy project. During the course of the year, three patents went to grant in the USA covering core-shell catalysts for fuel cells. These patents cover catalysts that are stable in the aggressive acidic environment of hydrogen fuel cells, while being active in the promotion of the chemical reactions necessary for converting hydrogen and oxygen into water. Ilika now maintains a portfolio of 22 patent families, comprising of 81 patents.
Materials Portfolio Activities
While the Company’s strategy has been to focus the majority of its resources on developing and commercialising its solid-state battery technology, Ilika was also active in the development of other energy materials, aerospace alloys and materials for electronics applications using its high throughput platform.
Energy Materials
In August 2016, Ilika announced that it is taking part in a three-year project to develop protected anodes for lithium sulphur batteries, led by Johnson Matthey Plc. This project is developing an innovative protected lithium anode approach to discover new electrolyte composition options and fabricate a free-standing, lithium-containing protected anode/separator for integration into pouch cells. The novel protected anode will mitigate a commonly experienced problem in lithium-sulphur cells, the so-called polysulphide shuttle effect, leading to enhanced performance cells that can be made with existing cell fabrication methods. The pouch cells being developed in this project are high capacity, low cost batteries for large scale renewable energy storage and therefore address a distinct market segment to the applications for which Ilika’s Stereax®batteries are designed. This project will complete in 2019.
In March 2017, Ilika announced a $1m, one year commercially-funded program with the Toyota Research Institute (‘TRI’) to develop game changing energy materials. The program is part of a $35 million investment by TRI over four years in research that uses artificial intelligence to accelerate the design and discovery of advanced materials. In this initial collaboration with the Company, Ilika’s unique high throughput platform was used to make and test candidate materials, which were identified using simulation, machine learning and artificial intelligence strategies. Ilika has now completed the initial screening activities associated with this phase of the project. Promising materials will be further scaled-up by Toyota and its suppliers for deployment in its future low-emission vehicles.
Aerospace Alloys
Ilika has continued in its lead role in a £2.15m, three year Innovate UK grant funded project with BAE Systems, GKN, Reliance Precision Engineering and the University of Sheffield. The project started in September 2015 to develop a new generation of self-healing alloys suitable for additive manufacturing (AM) processes and to develop a metallic manufacturing process that takes advantage of the flexibility of AM and the precision of subtractive manufacturing. This will enable the manufacture of novel components with critical feature tolerances, meeting the challenges faced in the design of mechanisms for the aerospace industry with lower weight, structural integrity and functional performance. The programme has been productive in defining new alloy systems of interest and a series of patent filings have been made.
In January 2018, Ilika completed its role leading a three year Innovate UK funded project with Rolls Royce, Diamond Light Source and the University of Cambridge to develop new superalloy compositions for gas turbine engines with better thermo efficiency than current alloys. The alloys are designed to increase gas turbine performance, reducing CO2 emissions and noise levels at take-off.
Electronic Materials
Ilika has continued its collaboration with Seagate, developing materials and processes for Hard Disk Drive (‘HDD’) applications. The project is focussed on materials with superior nanophotonic properties to achieve improved hard drive performance and reliability. These materials must operate at temperatures of up to 300⁰C for thousands of hours, requiring extremely robust nanomaterials that have specific photonic properties allowing light energy to be conducted.
In March 2018, Ilika announced an 18-month collaboration with PragmatIC and Arm to further progress development of ultra-thin and flexible semiconductors for mass market applications. The principal objective is to deliver P-type metal-oxide semiconductor circuit technology to enhance PragmatIC’s flexible integrated circuit designs. The first application is the smart packaging market which is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 8% to a projected value of $7.8billion by 2021.
Quality Management System
In January 2018, Ilika announced that its Quality Management System (QMS) for the development of solid-state batteries and materials research and development programmes has been assessed and found to meet the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 by DAS certification. ISO 9001 is the world’s most widely recognised QMS and helps organisations to meet the expectations and needs of their customers. The certification promotes the development of continual improvement, customer satisfaction, traceability and international best practices. Ilika aims to provide clients with the highest quality services and the ISO certification means that clients can have increased confidence in the service provided. The certification is independently audited annually.
Key performance indicators (‘KPIs’)
The board considers that the most important KPIs are technical and operational and relate to the sales pipeline and engagement of commercialisation partners resulting from the progress of the technical development programmes outlined above.
The most important financial KPIs are the cash position and the operating loss of the Group, which remain under constant focus and which are considered in the financial review.
FINANCIAL REVIEW
The Financial Review should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements of the Company and Ilika Technologies Limited (together the ‘Group’) and the notes thereto on pages 22 to 40. The consolidated financial statements are presented under International Financial Reporting Standards as adopted by the European Union. The financial statements of the Company continue to be prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as adopted by the EU and are set out on pages 41 to 45.
Statement of Comprehensive Income
Revenues
Revenue, all from continuing activities, for the year ended 30th April 2018 was £2.1m (2017: £1.1m). This includes £1.3m of grant income recognised from nine projects that the company has in progress with Innovate UK (2017: £0.7m from six programmes). Details of the various programmes are provided in the Materials Portfolio activities on page 5.
More of the Company’s activities are supported by grant or commercial funding than was the case in the prior year, where operational resources were more heavily devoted to the internally funded battery development programme.
Administrative expenses and losses for the period
Administrative costs for the year were slightly decreased at £3.8m in 2018 relative to £3.9m in 2017. This excludes the share-based payment charge.
Combined cost of sales and administrative expenses were £4.9m in the year which is up from the £4.4m for 2017 and is associated with the increased level of commercial and grant supported programmes.
2,173,210 Options lapsed in the year, of which 1,386,650 lapsed due to performance criteria. No reduction has been made in the share-based payment charge in respect of these lapsed options. 1,266,117 options were granted in the period.
The lower share-based payment charge together with the improved margin meant that loss on continuing activities before tax reduced from £3.9m in 2017 to £3.3m in 2018.
Statement of financial position and cash flows
At 30th April 2018, net assets amounted to £3.8m (2017: £6.2m), including net funds of £2.8m (2017: £5.4m).
The principal elements of the £2.6m decrease over the year ended 30 April 2018 in net funds were:
· Cash used in operations of £2.6m (2017: £3.2m);
· Purchase of plant, property and equipment of £0.3m (2017: £0.3m)
· Research and development tax credits received of £0.4m (2017: £0.4m);
PRINCIPAL RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES
Commercial risk
The Group is subject to competition from competitors who may develop more advanced and less expensive alternative technology platforms, both for existing materials and for those materials currently under development. The Group is largely dependent on its partners to commercialise the end-products containing the Group’s materials.
The Group seeks to reduce this risk by continually assessing competitive technologies and competitors. The Group seeks to commercialise materials through multiple channels to reduce overreliance on individual partners and, in agreements with partners, it ensures that there are commercialisation milestones which must be met for the partner to retain the rights to commercialise the materials.
Financial risk
The Group is reliant on a small number of significant customers and partners. Termination of these agreements could have a material adverse effect on the Group’s results or operations or financial condition. The Group expects to incur further operating losses as progress on development programmes continue.
The Group seeks to reduce this risk by broadening the number of customers and partners and thereby reduce reliance on individual significant companies. The Group applies for Research and Development tax credits to help mitigate its investment in these activities.
Intellectual property risk
The Group faces the risk that intellectual property rights necessary to exploit research and development efforts may not be adequately secured or defended. The Group’s intellectual property may also become obsolete before the products and services can be fully commercialised.
The Group seeks to reduce this risk by employing in-house staff with extensive global experience of patenting and licensing using commercially available patent searching and landscaping software. External patent agents and attorneys are used to advise on the drafting and filing of patent applications.
Dependence on senior management and key staff
Certain members of staff are considered vital to the successful development of the business. Failure to continue to attract and retain such highly skilled individuals could adversely affect operational results.
The Group seeks to reduce this risk by offering appropriate incentives to staff through competitive salary packages and participation in long-term share option schemes.
Brexit risk
The Group has reviewed the potential impact of Brexit on the risks identified above and believes that whilst intellectual property risk will remain largely unaffected, there may be an impact in the future regarding the Group’s ability to attract and retain highly skilled individuals.
The Group is alert to and continuously reviewing this potential risk and formulating its response at the appropriate time.